- Qinsun Instruments Co., Ltd.
- Tell:+86-21-6780 0179
- Phone:+86-17740808215
- Address:No. 2578 Minhang District Gu Dai Road, Shanghai
- Contact:Mr. Li
- QQ:846490659
What is a manual operated microtome?
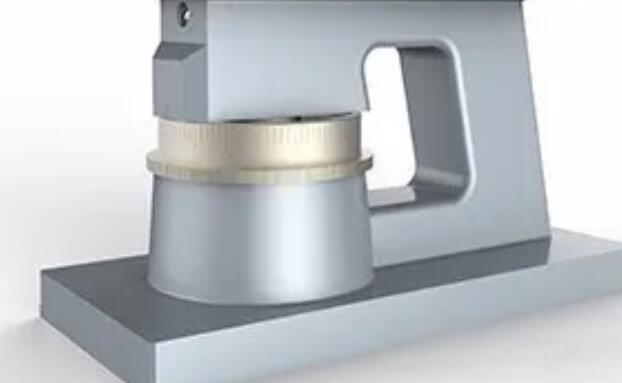
A manual operated microtome is a type of laboratory instrument used for cutting thin slices or sections of biological specimens for microscopic examination. It works by manually advancing a sample block containing the specimen across a sharp blade to produce thin slices.
The microtome consists of a base, a sample holder, a cutting blade or knife, and a mechanism for advancing the sample block. The sample block is typically made of paraffin or other embedding material that supports the specimen during cutting. The blade is usually made of steel or diamond and can be adjusted for the thickness of the slices.

To use a manual operated microtome, the specimen is first embedded in a block of paraffin or other material. The block is then mounted on the microtome and secured in the sample holder. The microtome blade is adjusted to the desired thickness, and the sample block is advanced across the blade to produce thin slices. The slices can then be mounted on a microscope slide and stained for examination under a microscope.
Manual operated microtomes are commonly used in histology and pathology laboratories for preparing thin sections of tissue samples for diagnosis. They are also used in research laboratories for preparing thin sections of specimens for analysis. While manual operated microtomes require skilled operators and are more time-consuming than automated microtomes, they are still used today because they offer greater precision and control over the cutting process.





